Top AI Achievements of 2025
2025 changed everything. The "next big thing" is now the "current essential tool." This article cuts through the noise. We delivered the Top AI Achievements of 2025. For the skeptic: see the proven results. For the leader: find your competitive edge. Read on. The future won't wait.

2025 wasn't another incremental year for AI. It was a tectonic shift. This is the year artificial intelligence stopped being just a tool and started becoming a transformative partner in discovery.
The Rising Hype of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence has quickly moved from a futuristic idea to a key part of modern business. Breakthroughs in generative AI and agentic systems have sparked huge excitement. This has led to rapid adoption and massive investments as companies compete to gain advantages in innovation, efficiency, and growth. Top research firms back this trend with strong data on usage, spending, economic impact, and future plans.
- According to McKinsey's 2025 State of AI survey, 88% of organizations now regularly use AI in at least one business function—up from 78% the previous year—signaling that AI has firmly transitioned from pilot projects to operational reality.
- Gartner forecasts that worldwide spending on AI will reach nearly $1.5 trillion in 2025. It is propelled by massive investments in AI-optimized hardware, software, services, and integrated products such as AI-enabled smartphones and PCs.
- PwC estimates that AI could add up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030. The largest share coming from productivity improvements across sectors.
Let’s discuss the Top AI Achievements of 2025. We will move beyond the headlines to show you the tangible breakthroughs that are redefining what's possible in health, quantum science, robotics, and beyond.
1. Healthcare
1.1. The Challenge of Unseen Cancer Networks
Cancer progression is driven by complex, hidden interactions within our cells, specifically between microRNAs (miRNAs) and messenger RNAs (mRNAs). These interactions form vast, post-transcriptional regulatory networks that control gene behavior. However, identifying which specific sets of these interactions are reliably linked to a disease like cancer is a major challenge. Existing methods often produce high false-positive rates or lack the ability to transform biological data into practical, predictive models for new patients.
Working Strategy
RNACOREX, an open-source tool, tackles this problem. It uses a novel; two-pronged computational pipelines designed to find and validate robust interaction networks:
Step 1: Biological Plausibility Filter: The tool first filters all possible miRNA-mRNA interactions through curated scientific databases (like TargetScan and miRTarBase). It only keeps interactions that have prior biological support, either through prediction or experimental validation. This way, it drastically reduces spurious candidates.
Step 2: Dual-Score Integration: For each candidate interaction, RNACOREX computes two scores:
- A Structural Information Score based on existing biological knowledge.
- A Functional Information Score that measures the empirical association between the interaction and a clinical outcome (like patient survival) using expression data from sources like The Cancer Genome Atlas.
Step 3: Model Building & Validation: These scores are integrated to rank interactions. The top-ranked network is then used to build a Conditional Linear Gaussian (CLG) classifier—a probabilistic AI model that can predict outcomes for new, unseen patient data. Simultaneously, it can validate the biological relevance of the discovered network.
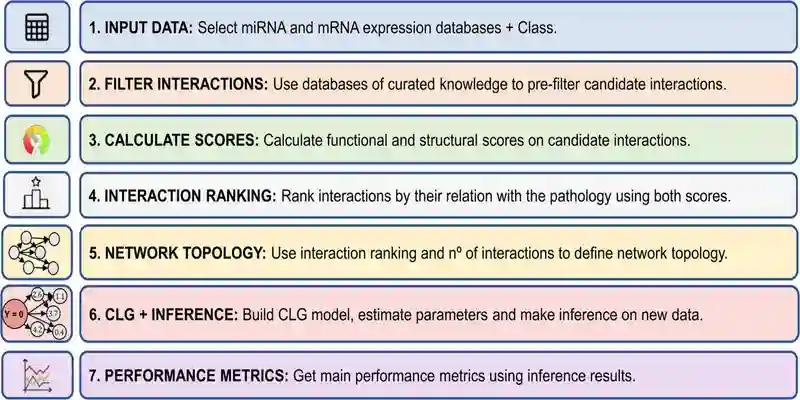
RNA coregulatory network explorer and classifier Image Source
Benefit
The tool bridges prediction with biological insight. It achieves competitive accuracy in classifying cancers like survival time. Plus, it reveals the specific molecular interactions that drive the disease which offers researchers clear targets for further study.
1.2. New Breakthrough for Predicting Results at Shockingly Close to Reality
Traditional prediction models, like the widely used least-squares method, are primarily optimized to minimize average error. While effective, this approach can sometimes miss a crucial objective: ensuring that predicted values align perfectly on a 1-to-1 scale with actual, real-world measurements. Researchers have now developed a new technique, the Maximum Agreement Linear Predictor (MALP), which shifts the goal from simply being "close" to achieving the highest possible agreement with reality. This is especially vital in fields like healthcare, where predictions must directly correspond to true biological values for reliable diagnosis and patient monitoring.

Working Strategy
The core innovation of MALP is its unique optimization target. Instead of minimizing error, it is mathematically designed to maximize the Concordance Correlation Coefficient (CCC). The CCC is a statistical measure that specifically evaluates how well pairs of predicted and actual data points fall along a perfect 45-degree line on a scatter plot. This means it simultaneously measures both precision (how tight the cluster is) and accuracy (how close it is to the true 1:1 line). The method was validated using real medical data, such as translating eye scan measurements between old and new optical coherence tomography (OCT) devices and estimating body fat percentage from simpler body measurements, where it consistently produced predictions with superior alignment to the true values.
Benefit
The key benefit of this breakthrough is the delivery of more trustworthy and directly usable predictions in scientific and medical contexts. When tested, MALP produced results that were "shockingly close" to actual measurements, often outperforming classic approaches in terms of alignment.
1.3. Decoding the Cellular Machine: A Novel Approach
In January 2025, researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons introduced an artificial intelligence system. It is capable of predicting gene activity inside human cells, effectively revealing how cells operate at a fundamental level. This approach, detailed in Nature, marks a shift from descriptive biology to predictive computational biology. It has the potential to transform understanding of diseases such as cancer and genetic disorders.
Working Strategy
The team, led by Professor Raul Rabadan, trained a machine learning model on gene expression and genomic accessibility data from over 1.3 million normal human cells. By learning the “grammar” of gene regulation across diverse cell states—similar to how large language models learn linguistic patterns—the system can accurately predict which genes are active in cell types it has not previously encountered. The model’s predictions align closely with experimental results. Additionally, using this AI, researchers identified mechanisms disrupted by mutations in a pediatric leukemia case. It demonstrated the model’s ability to uncover biological drivers of disease.
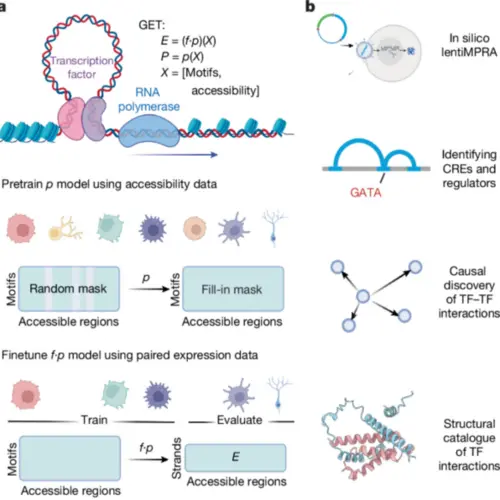
Image Source: Nature article
Benefit
This AI-driven method offers significant advantages for biomedical research:
- It enables large-scale computational experiments
- Accelerates discovery of how cell behavior changes in disease
- Helps illuminate poorly understood regions of the genome (“dark matter”).
This technique provides detailed predictive insights into gene activity and mutation effects. The given technology also helps identify new therapeutic targets and deepen understanding of complex diseases beyond cancer.
2. Quantum Science
2.1. Sound Waves Extend Quantum Memory Lifetimes
In August 2025, researchers at the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) reported a major advance in quantum information technology. It is a hybrid quantum memory that uses sound waves to store quantum states significantly longer than current approaches. The breakthrough addresses a core limitation of superconducting qubits which are excellent for rapid computation but poor at retaining information over time. The new approach can convert electrical quantum information into acoustic vibrations, extending memory lifetimes by up to 30 times. This work was published in Nature Physics by a team led by graduate students Alkim Bozkurt and Omid Golami under the supervision of Professor Mohammad Mirhosseini.

Working Strategy
The Caltech team developed a hybrid system combining a superconducting qubit with a mechanical oscillator. It effectively functions like a microscopic tuning fork that vibrates with sound waves at gigahertz frequencies. Quantum information encoded in electrical signals is transferred into phonons—quantized units of vibrational energy—which serve as the memory medium. Because these phonons operate at the same high frequency and persist longer under cryogenic conditions, they allow quantum states to be “stored” and later “remembered.” The researchers measured the decay of quantum information in this mechanical oscillator and found that it retains information approximately 30 times longer than traditional superconducting qubits.
Benefit
Extended storage times improve the feasibility of complex quantum computation and error correction. It potentially benefits fields such as secure communications, drug discovery, and large-scale simulations in healthcare and materials science.
The slower propagation of sound compared to electromagnetic signals also enables more compact device designs, reduces energy leakage, and supports integration of multiple memory elements on a single chip.
2.2. Turning Ultra-Thin Metasurfaces into Quantum Processors
Harvard SEAS researchers demonstrated that metasurfaces — ultra-thin, nanoscale patterned surfaces — can serve as quantum optical processors. They can entangle photons on a single flat chip, potentially replacing bulky conventional optical components. Photons are capable of encoding and processing information at room temperature. Traditionally, they require complex optical networks of waveguides, lenses, mirrors, and beam splitters, which are difficult to scale.
Working Strategy
The researchers fabricated metasurfaces with nanoscale patterns that control light on an ultra-thin platform. It then generates entangled photon states to carry out quantum operations. They applied graph theory to design the metasurface. This mathematical approach models photon interactions as connected nodes and pathways. Hence, it enables prediction and control of how photons interfere and entangle. The approach compresses the functions of a full linear optical network into a single, stable, scalable metasurface.
Benefit
Metasurface-based quantum photonics offers compact, robust, and scalable quantum processors. This platform could accelerate development of room-temperature quantum computers and networks.
2.3. Level-Zero Distillation Shrinks Quantum Resource Costs
Researchers at the University of Osaka developed a novel zero-level magic state distillation method. It significantly improves the efficiency of preparing magic states—a fundamental requirement for fault-tolerant quantum computing. Magic state distillation enables universal quantum computing by converting many noisy states into a high-fidelity magic state. The new approach carries out distillation at the physical qubit (zeroth) level. It dramatically reduces spatial and temporal overhead compared with traditional logical-level methods.
Working Strategy
The team engineered a zero-level distillation circuit that operates directly on physical qubits. These were arranged on a square lattice using nearest-neighbor two-qubit gates and the Steane code for error detection. Instead of performing distillation after full error correction on logical qubits, the protocol distills high-fidelity magic states early in the computation. After it, teleports or maps these states to surface codes for use in fault-tolerant operations.
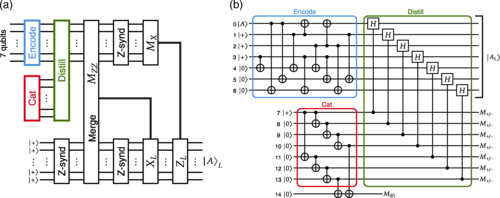
Benefit
Zero-level distillation substantially reduces the number of qubits and computational steps required compared with logical-level protocols. The lower resource demands and reduced error overhead make early and full-scale fault-tolerant universal quantum computing.
2.4. The Deep Freeze: A New Chill for Quantum Stability
The incredible potential of quantum computers is locked behind a wall of extreme cold. To function, their delicate quantum bits, or qubits, must be shielded from all thermal noise and interference. It is a state that’s only achievable at temperatures a fraction of a degree above absolute zero. Achieving and maintaining this "deep freeze" has been one of the most significant and costly engineering bottlenecks. It limits the scalability and reliability of quantum systems. A breakthrough from researchers has now engineered a specialized quantum refrigerator that autonomously cools superconducting qubits to record-low temperatures. Hence, providing the ultra-stable environment they desperately need to perform complex, error-free calculations.
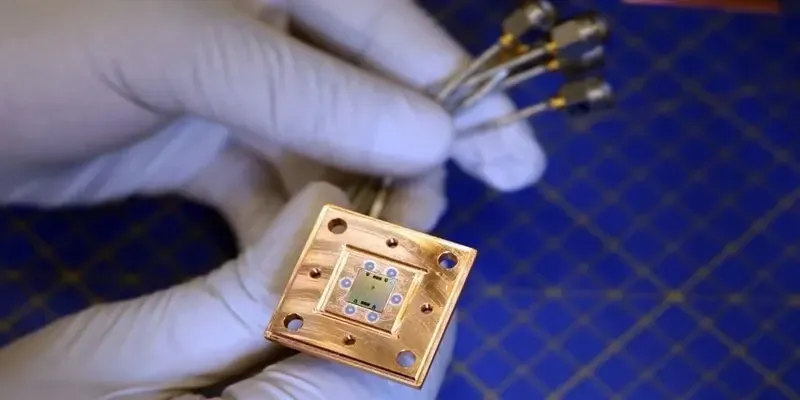
Working Strategy
The core of this innovation is an on-chip, autonomous refrigeration system designed specifically for superconducting quantum circuits. Unlike large, external dilution refrigerators, this new device integrates directly into the quantum computing architecture.
Its strategy is based on evaporative cooling at the microscopic scale. The system uses a carefully engineered circuit element that mimics a "hot" reservoir. By precisely manipulating the quantum states of individual microwave photons (particles of light), the refrigerator forces these energy particles to carry heat away from the qubit. It effectively then pumps the entropy out of the system. This process continuously drains thermal energy, actively cooling the qubit to temperatures below what passive systems can achieve. Plus, it maintains that stable, ultra-cold state autonomously.
Benefit
By pushing temperatures to new lows, the refrigerator dramatically reduces thermal noise. This innovation is a key step toward building larger, more complex quantum processors with hundreds or thousands of reliably cooled qubits.
3. Deepfakes
3.1. Beyond the Face: Hunting Deepfakes in the Shadows
The deepfake threat is evolving faster than our ability to detect it. While current tools excel at spotting manipulated faces, they are easily fooled by a simple trick: removing the face from the video. Sophisticated AI can now generate entirely convincing fake footage of events, objects, or people from behind, leaving traditional detectors blind. A groundbreaking collaboration between UC Riverside and Google has risen to this challenge with a new system called UNITE (Universal and Transferable Deepfake Detection). This "deepfake hunter" represents a paradigm shift by looking beyond the subject to analyze the entire digital scene. It aims to expose forgeries that current technology would miss completely.
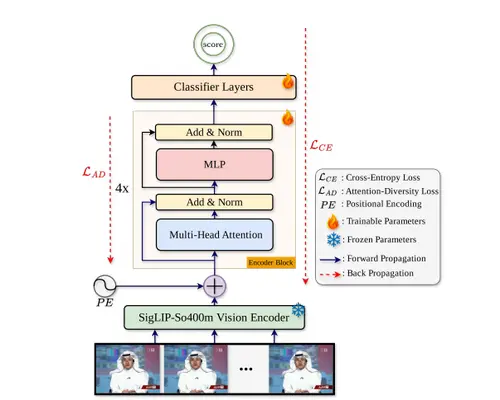
Working Strategy
UNITE's power lies in its universal and holistic analysis framework, which operates in two key phases to achieve unprecedented detection accuracy.
Phase 1: Multi-Cue Forensic Analysis: Instead of focusing solely on facial artifacts, UNITE is trained to be a digital scene investigator. It simultaneously scans for subtle, unnatural inconsistencies across multiple dimensions:
- Background Geometry: Analyzing spatial layouts and perspectives for physical impossibilities.
- Temporal Motions: Detecting unnatural movement patterns or fluid dynamics in objects and environments.
- Global Statistical Noise: Identifying the unique "digital fingerprints" and noise patterns left by different AI generation models across the entire video frame.
Phase 2: Knowledge Transfer via Pre-Training: The system is first pre-trained on a massive, diverse dataset of AI-generated content. It allows it to learn the fundamental "tells" of synthetic media. This learned knowledge is then transferred and fine-tuned to detect new, unseen deepfake methods. It makes it adaptable to evolving threats without requiring retraining from scratch for every new forgery technique.
Benefit
The deployment of a tool like UNITE provides a critical line of defense with wide-ranging benefits for information integrity.
- UNITE neutralizes a primary evasion tactic used by forgers. It significantly raises the barrier for creating undetectable misinformation.
- UNITE offers a more future-proof solution compared to narrow, easily obsolete detectors.
- Plus, it provides a powerful tool to audit content, flag potential fakes, and help protect public discourse from AI-powered deception.
4. Robotics
4.1. The Sentient Surface: Giving Robots a New Sense of Touch
Today's robots can see and move with incredible precision, but they operate in a world without feeling. Their inability to perceive touch, temperature, or pressure safely limits their interaction with fragile objects and unpredictable environments. Researchers have now created a breakthrough in robotic sensory perception: a novel, intelligent "skin" that endows machines with a rich, human-like sense of touch. This innovation transforms the entire surface of a robot into a unified, sensitive organ. It can sense nuanced stimuli like heat and potential damage, paving the way for a new generation of collaborative and responsive machines.

Working Strategy
The core of this breakthrough is not a network of disparate sensors but a single, elegant material: a specially engineered ionic hydrogel. This flexible, jelly-like substance is the foundation for a simple yet powerful sensing strategy.
- Unified Sensory Material: The hydrogel itself is electrically conductive. When this material is deformed by pressure, stretched, or exposed to temperature changes, its electrical properties change in a specific, measurable way.
- Data-Rich Signal Interpretation: Electrodes connected to the skin capture these subtle electrical changes. Advanced machine learning algorithms are then trained to interpret this complex signal data. By analyzing patterns in the electrical resistance and capacitance, the system can distinguish between different types of stimuli—such as a gentle touch, a sharp poke (pain), or a hot surface—all from the same piece of material. It does not need separate dedicated sensors for each sense.
Benefit
This multi-sensory skin solves fundamental problems in robotics like:
- By detecting excessive pressure (potential crushing) and high temperature (potential burns), the skin allows robots to instantly react to avoid causing harm. It is critical for robots working alongside people in factories, care homes, or as prosthetics.
- They can feel texture, gauge grip pressure, and sense slip to handle fragile items—like an egg, surgical tool, or an elderly person's arm. With a delicacy and confidence previously impossible, this innovation revolutionizes automation in logistics, agriculture, and medicine.
- These robots use a single, low-cost gel material to replace an array of specialized sensors previously used.
4.2. A Tape Measure's Second Act: The Gentle Giant of Farm Robotics
The multi-billion-dollar challenge of agricultural harvesting has long stumped roboticists. Delicate fruits and vegetables like tomatoes, strawberries, and bell peppers require a grip that is both gentle enough to avoid bruising and precise enough to detach the produce. Traditional rigid grippers often cause damage, while soft grippers can lack control.
Engineers at UC San Diego have found an ingenious and unexpectedly simple solution in a common household item: the retractable measuring tape. By reimagining its flexible yet controllable coil, they have created a novel robotic gripper. It combines a soft touch with reliable, low-cost mechanics to solve one of automation's trickiest tasks.
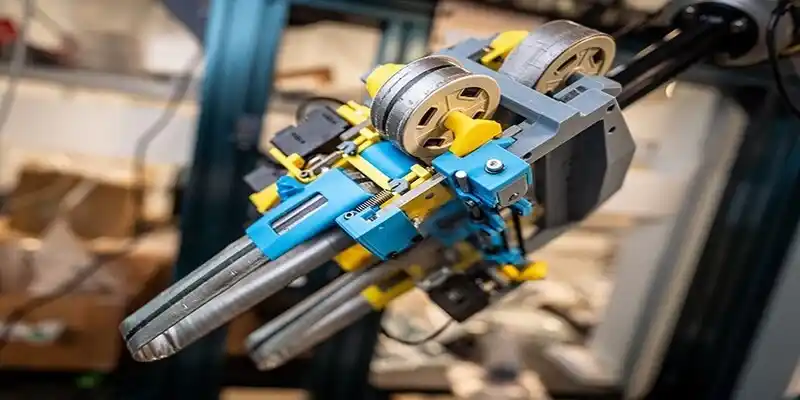

Working Strategy
The intuitive behavior of a measuring tape is changed into a reliable gripping mechanism. It acts as a 3D-printed "finger."
Each gripper "finger" is built around a segment of standard steel measuring tape. When a small motor pulls the free end of the tape, it retracts. Moreover, it naturally curls into a tight, consistent coil due to its pre-stressed metal construction. This curling motion is the heart of the grip. As the tape coils, it conforms to the shape of the target object. Whether it's a round apple or an oblong eggplant. The coil wraps around the produce, distributing pressure evenly across a wide surface area instead of pinching at a few points.
The entire assembly is remarkably simple, consisting primarily of:
- The tape
- A motor to actuate it
- And a 3D-printed housing to guide the curl.
It avoids the need for complex arrays of sensors, pneumatic systems, or expensive custom materials.
Benefits
The primary benefit of this measuring tape gripper is its ability to solve the core dilemma of agricultural robotics. It prevents bruising and damage to delicate produce like tomatoes and strawberries to reduce food waste and increases crop value. Its ingenious use of low-cost, off-the-shelf components like steel tape and basic motors makes it an affordable and scalable solution for farms, lowering the barrier to automation.
4.3. The High-Stakes Game of Robotic Grasp
For a robot, picking up an object isn't simple. It needs to know not just what the object is, but its exact orientation in 3D space. This concept is known as its 6D pose (position + rotation). In dynamic, real-world environments like warehouses or factories, objects are rarely perfectly aligned. Traditional robotic vision systems often struggle with this, leading to failed grasps, dropped items, and production delays. A groundbreaking new dataset has been developed to tackle this precise challenge. It teaches robots to perceive the world with the spatial understanding they need to grasp reliably on the first try.
Working Strategy
The core strategy of this achievement is to create a superior training and testing foundation. Researchers constructed a dataset that mirrors the complex conditions robots face on a real factory floor.
The dataset pairs high-resolution RGB (color) images with precise depth (distance) maps. This combination lets AI models to understand both the visual texture of objects and their exact three-dimensional shape and position.
The dataset doesn't just show objects in perfect, easy-to-grasp positions. It includes extensive viewpoint variations and complex occlusion scenarios. It forces the AI to learn robust pose estimation from incomplete visual information.
Credit: Phan Xuan Tan from SIT, Japan
Benefits
The primary benefit of this 6D pose dataset is its power to dramatically improve the core intelligence of robotic grasping systems. By training AI models on its rich, challenging data, robots develop a much more accurate understanding of an object's 3D position and orientation.
It leads directly to a:
- Higher success rate for first-attempt picks
- Fewer dropped items
- And smoother operation in logistics and assembly.
Furthermore, its enhanced adaptability for cluttered, real-world environments reduces the need for costly, pre-sorted workstations. It also accelerates the deployment of reliable productive automation across industries.
4.4. The Mechanical Bee: Taking Flight to Secure Our Food Future
The global decline of natural pollinators like bees poses a direct and serious threat to agricultural food production. While drones exist, they are too large, energy-inefficient, and disruptive to navigate the delicate ecosystems of a flowering crop field. Engineers have now made a pivotal breakthrough in bio-inspired microrobotics: a fast, agile, and incredibly enduring robotic insect. This tiny machine isn't just a lab curiosity; it's designed with a critical mission in mind: to mimic the flight of a bee and potentially serve as an artificial pollinator. It offers a high-tech insurance policy for our food systems in a changing world.

Credit: Courtesy of the researchers
Working Strategy
The revolutionary performance of this robotic insect stems from a fundamental re-engineering of its core propulsion system.
The robot is powered by soft electrohydraulic actuators unlike traditional rigid motors or inefficient electromagnetic actuators. These work like artificial muscles; when a voltage is applied, they rapidly change shape, hence, flapping the robot's lightweight wings.
This "muscle" technology is the key to its performance. It allows for very high-frequency wing flapping to generate the necessary lift and thrust for agile flight. More importantly, this system is extraordinarily energy-efficient. It consumes significantly less power per wingbeat than older technologies.
Integrated Design for Stability: The actuators, wings, and a minimalist control system are all integrated into an ultra-lightweight chassis. So, the robot not just fly, it also executes precise, stable maneuvers like sharp turns and hovering.
Benefit
The robotic insect's core benefit lies in its unprecedented endurance and agility at a tiny scale. These robots can fly over 100 times longer than previous models to move from lab demo toward real-world use. This breakthrough makes the long-envisioned application of mechanical pollination viable. Hence, it offers a high-tech safeguard for food security against bee population decline.
5. AI-Models
5.1. The "One-Shot" Data Scientist: AI That Thinks with Tables
Tabular data, a classic spreadsheet of rows and columns found in everything from medical records to financial reports. In data science, tabular data remains the most common format. However, advanced deep learning models often struggle with these structured datasets. Especially, when they are small (under 10,000 samples) and require extensive tuning and time. A breakthrough new model, TabPFN (Tabular Prior-Data Fitted Network), flips this paradigm. Instead of training from scratch on a user's small dataset, TabPFN arrives pre-trained with a kind of "common sense" for tabular reasoning. It can analyze a new dataset and make highly accurate predictions in seconds. Moreover, it acts as an instant AI data scientist for everyday analytical problems.
Working Strategy
TabPFN's power comes from a revolutionary two-stage training strategy. It separates learning general principles from applying them to a specific case.
Before ever seeing real user data, TabPFN is trained on a massive, artificially generated universe of potential tabular datasets. Researchers designed this synthetic data to cover an incredibly wide space of possible statistical relationships, patterns, and causal structures like in real-world tables.
This exhaustive pre-training allows TabPFN to learn a powerful, generalized understanding of how data in tables correlates. When presented with a new, small real-world dataset (e.g., a few hundred patient records), it doesn't need traditional training. Instead, it performs in-context inference.
It rapidly analyzes:
- The new data's structure
- Compares it to the patterns it learned from the synthetic universe
- And "reasons" its way to a prediction.
It does it all in a single forward pass of the neural network.
Benefit
TabPFN delivers state-of-the-art predictive accuracy on small, real-world datasets in seconds. Hence, it eliminates the days of manual tuning required by traditional models. It specifically solves the pervasive "small data" problem, making powerful AI accessible for scientific research, medical studies, and business analytics.
5.2. Beyond the Algorithm: Rethinking Intelligence from the Ground Up
The current trajectory of artificial intelligence is often critiqued as being built on a narrow, Western-centric foundation. A groundbreaking international research initiative, Abundant Intelligences, is challenging this paradigm at its core. Led by Concordia University, this program argues that the very definition of "intelligence" in AI must be expanded. It seeks not just to tweak algorithms, but to fundamentally "Indigenize" the field by integrating diverse Indigenous knowledge systems.
Working Strategy
The strategy of the Abundant Intelligences program is interdisciplinary and foundational. It focuses on changing the process of AI creation rather than deploying a single tool.
The core methodology involves bringing Indigenous scholars, elders, and community members into the research process as lead partners. Their knowledge systems—which view intelligence as embedded in relationships with land, community, and spirit—are not treated as mere data points. These are essential frameworks for re-conceptualizing what AI is and should be.
The program works to co-create new research and design methodologies that embed Indigenous principles like:
- Relational accountability
- Reciprocity
- And respect for context.
It could mean developing AI models that prioritize long-term ecosystem health over short-term efficiency. Plus, data governance models that respect Indigenous data sovereignty.
Benefit
This initiative makes AI fairer and less harmful by including diverse cultural views. It unlocks new, sustainable solutions to global problems like climate change by applying Indigenous knowledge. Ultimately, it strengthens the entire field of AI, making it more creative and useful for all of humanity.
Conclusion
The Top AI Achievements of 2025 demonstrate that the field's progress is no longer just about raw computational power or isolated benchmarks. This year's pivotal breakthroughs reveal a powerful and necessary trend: the integration of AI across the entire scientific and technological stack. From healthcare and quantum science to robotics and model development, these advances show that AI has become the essential, connective tissue of innovation. In healthcare, we see AI moving from simple diagnosis to uncovering the fundamental biological networks of disease. In quantum computing, AI and new engineering feats are solving the core hardware challenges of stability and error correction. Robotics is achieving new levels of delicate, real-world interaction. Lastly, new AI models themselves are becoming faster, more accessible, and more culturally aware. Together, these achievements of AI in 2025 signal a shift towards more capable, efficient, and impactful intelligent systems.


